Customize content controls
Content controls help users create templates in Microsoft Word. From a WorkZone point of view, a content control represents a specific property of an entry. An entry is an object in OData that refers to the database. Entries in OData are used to retrieve specific values from the database.
When a user creates a template, the user inserts content controls by selecting menu items from the Content properties group on the Insert tab in Word. The user then selects a document in the Registration pane and clicks Merge. WorkZone substitutes each content control with values from the database.
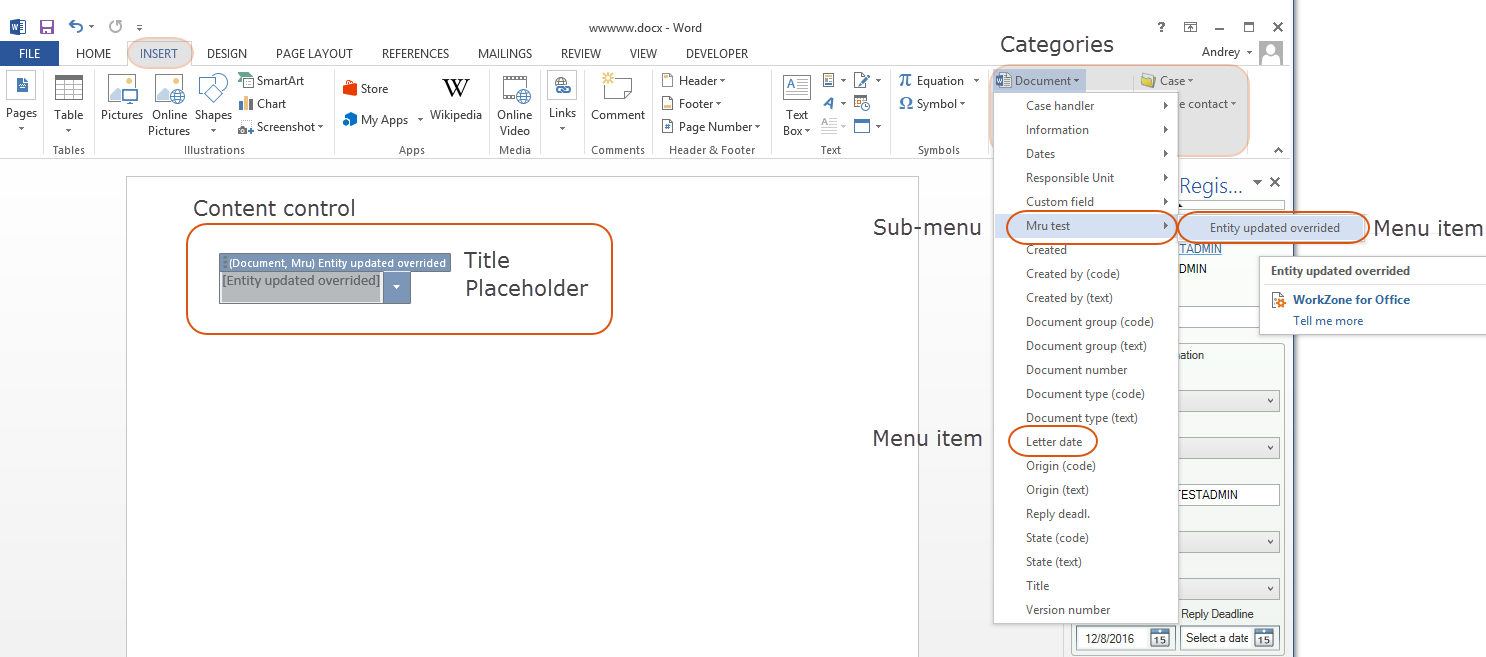
You can create sub-menus and define which menu items to be displayed in each category. Content properties are divided into four categories:
- Document
- Case
- Document contact
- Case contact
Create a content control
This section describes step by step how to create a new content control called Entity updated overrided. The content control represents the Entity updated property of the MruRecords entry. To complete the creation, you need to create a reference to the database through OData and add a new menu item that will appear in Word.
Define the content control in OData
- Open the merge_odata_description XML file. To request a specific entry, create a query to OData. Use the following example:
staticData– use this element to request an entry.E34FE056-129F-46D2-B7E7-A20D91F9F47C– insert a unique ID that will be used internally as a reference to the OData entry.query– an OData request that retrieves the entry that you need. In this example, it is a call to theMruRecordsentry.- Within the
staticDataelement, bind a content control with the required property. To do this, you need to add and define the property element.You may add as many properties as you need.
<staticData id="E34FE056-129F-46D2-B7E7-A20D91F9F47C" query="MruRecords?$filter=Value eq '{recordId}' and User_Value eq '{record.officer}'"> <property id="C5D4237E-2DEF-4D5A-B714-1F5CA88518F5" name="EntityUpdated " /> </staticData> property– use this element to request a property.E34FE056-129F-46D2-B7E7-A20D91F9F47C– insert a unique ID that will be used internally as a reference to the property of the entry.name– specify property's name in OData.- Add a new menu item to the Word application. You can do this in the menu_description XML file. Open the file and find a proper place for the new menu item. The current example represents how to search for the Document category.
<menu id="Case">refers to Case.<menu id="Record">refers to Document.<menu id="CaseParty">refers to Case contacts.<menu id="RecordParty">refers to Document contacts.menu– use this element to create a sub-menu.displayName– define a menu item name to be displayed in Word.dynamicMenu– use this element to create new menu items.ref– specify reference to the unique ID in themerge_odata_descriptionXML file.- Optionally, define customized names for the new menu item and content control:
<label dataItemRef="C5D4237E-2DEF-4D5A-B714-1F5CA88518F5"> <value xml:lang="en-GB">Entity updated overrided</value> <value xml:lang="da-DK">Entity updated overrided</value> </label>where:
label– specifies a customized name.- dataItemRef – specifies a reference to the property of the entry from the merge_odata_description XML file.
xml:lang– is a localization parameter.
- You can define how the content control must behave in Word when there is no value. You have two options:
- Keep the content control with no changes
- Hide the content control
For option a, specify the unique ID of the entry within the
<Rule rule="Unchanged">section.For option b, specify the unique ID of the entry within the
<Rule rule="Empty">section.Example:
<Rule rule="Unchanged"> <menuDataRefs> <ref>E34FE056-129F-46D2-B7E7-A20D91F9F47C</ref> </menuDataRefs> </Rule> <Rule rule="Empty"> <menuDataRefs> <ref>17EDE3E5-43D3-4B88-8E6E-F336D916B916</ref> </menuDataRefs> </Rule> ref– a reference to the unique ID in the merge_odata_description XML file.-
Optionally, you can define which information that should be included in the content control title.
Example:
<cc dynamicMenuRef="Mru_Items"> <titleFormat xml:lang="en-GB">(Document, Mru) {displayName}</titleFormat> <titleFormat xml:lang="da-DK">(Document, Mru) {displayName}</titleFormat> </cc>where:
dynamicMenuRef– specifies a reference to a menu item.TitleFormat– defines the content control title for each language.{displayName}– displays the name of the menu item that a user can click.
<staticData id="E34FE056-129F-46D2-B7E7-A20D91F9F47C" query="MruRecords?$filter=Value eq
'{recordId}' and User_Value eq '{record.officer}'">where:
You may use any unique ID, however, it is recommended to use a GUID generator to generate the ID.
where:
Add content control to the user interface
In the code source, the Document category refers to Record. Therefore, the new sub-menu must be added under the <menu id="Record"> element:
<menu id="Mru">
<displayName xml:lang="en-GB">Mru test</displayName>
<displayName xml:lang="da-DK">Mru test</displayName>
<dynamicMenu id="Mru_Items">
<contentRefs>
<ref>E34FE056-129F-46D2-B7E7-A20D91F9F47C</ref>
</contentRefs>
</dynamicMenu>
</menu>;where:
where:
